What is Base Excision Repair (BER)?
A normal or cancer cells pathway to repair single DNA strand brakes.
Uses Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) proteins to flag the damages and carry out its repairing.
Any DNA single strand DNA brake is quickly detected by the mitochondria, which then notifies the PARP proteins, that quickly replace the missing base with the correct one.
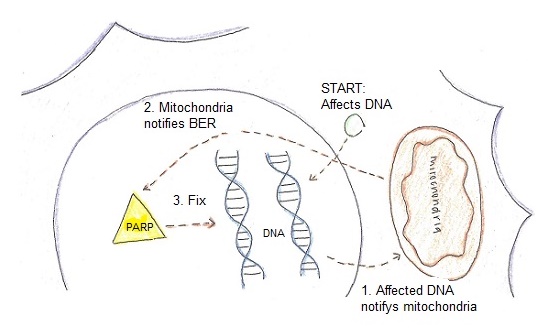
This image shows how BER works in response to a faulty DNA.
1. The damaged DNA sends signals to the mitochondria.
2. The mitochondria notifies the PARP proteins in the nucleus to fix the single strand break in the DNA.
3. The PARP proteins perform the base excision repair by changing out the damaged base and replacing it with new one.
4. The DNA is repaired and the cell survives.
With the knowelege of BER, we can better understand genes and how this repair process can be manipulated to become the future of anti-cancer treatments, especially melanoma.