Impact
Pathogenic Infections
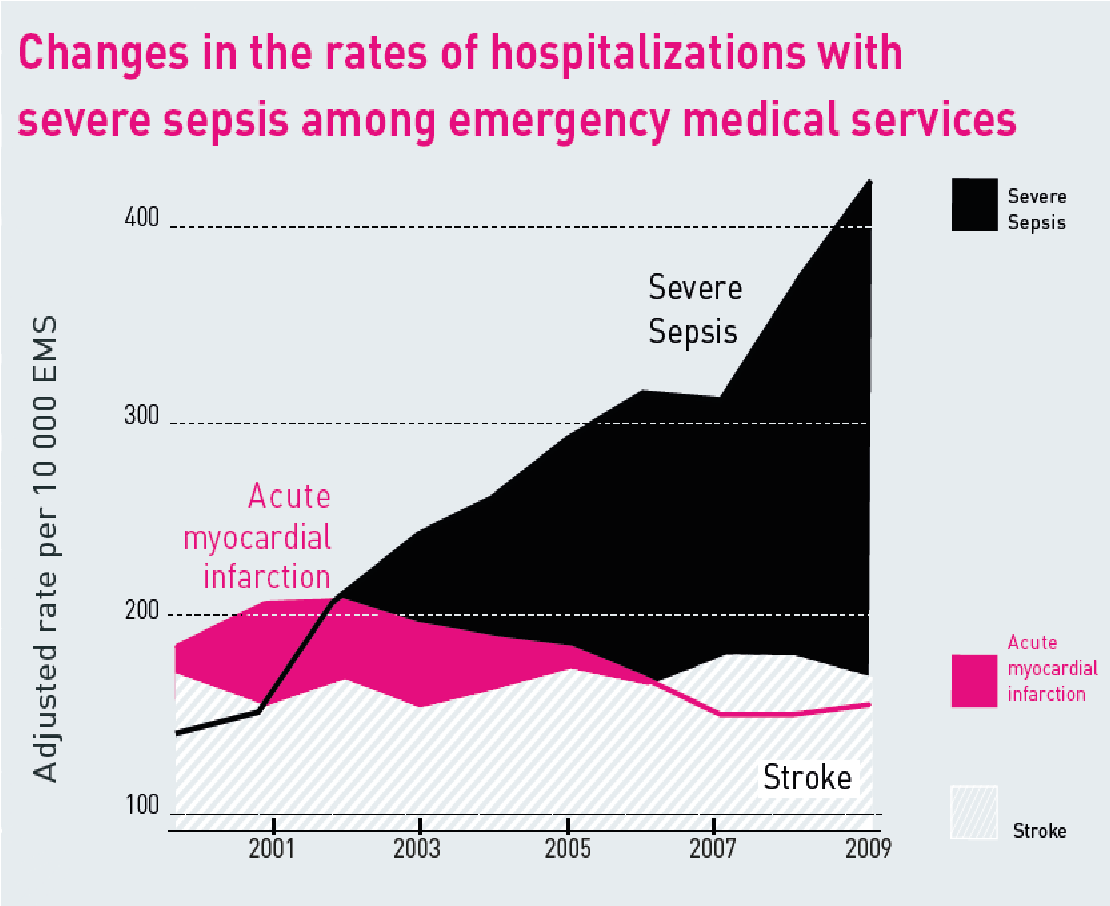
- Sepsis: the EMCD can save millions of patients worldwide with its efficient removal of all pathogens
in the bloodstream, preventing any sort of inflammation
- HIV/AIDS: the EMCD will be able to bind to the HIV virus, reducing proliferation and progression to AIDS.
It also helps HIV/AIDS patients to survive pathogenic attacks even with their weak immune system
- Immunodeficiency Disorders: people born with immunodeficiency disorders will have an easy, efficient,
and quick process to rid their blood of pathogens
- Organ Transplants: the EMCD allows for the immunosuppressant to do its job without placing the patient at extreme risk
- Other Bacterial and Viral Diseases: the EMCD quickly and completely removes the pathogens from the body
It also helps HIV/AIDS patients to survive pathogenic attacks even with their weak immune system
Antibiotics
- no need to identify the pathogen before treatment as MBLs can bind to a wide variety of pathogens and toxins
- the EMCD completely eliminates the bacteria unlike antibiotic treatments, removing any debris to help reduce the over-excited inflammatory response
- the EMCD does not contribute to antibiotic resistance
Economy
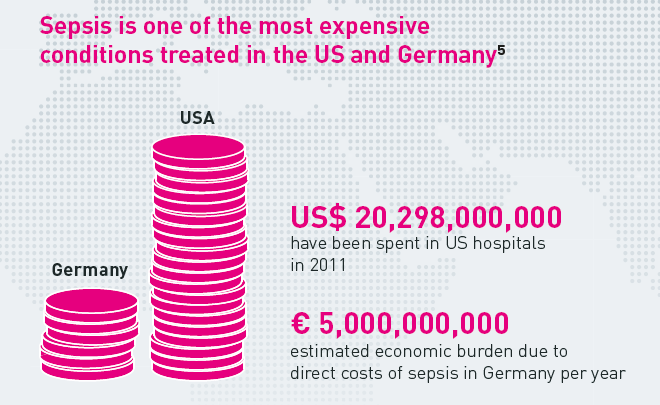
- Sepsis is the most expensive medical condition. Hospitals in the United States spend over $20,000,000 annually to treat 1,600,000 million sepsis patients
- Lifetime Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) for HIV/AIDS costs around $367,134 per person
- The EMCD is a cheap solution to both, as the genetically modified MBLs comprise the majority of its cost.
However, the MBLs, like all other aspects of the EMCD, can easily be mass produced.